
ACADEMIC

BIOLOGY
PLANT CELLS
Helpful Websites, Interactives, and Videos on Cell Organelles:

Plant Cell Organelles
The following are examples of structures and organelles that can be found in typical plant cells:
-
Cell (Plasma) Membrane: This thin, semi-permeable membrane surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosing its contents.
-
Cell Wall: This rigid outer covering of the cell protects the plant cell and gives it shape.
-
Chloroplast: Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis in a plant cell. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs energy from sunlight.
-
Cytoskeleton: This network of fibers throughout the cytoplasm helps the cell maintain its shape and gives support to the cell.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is an extensive network of membranes composed of both regions with ribosomes (rough ER) and regions without ribosomes (smooth ER). The ER synthesizes proteins and lipids.
-
Golgi Complex: This organelle is responsible for manufacturing, storing and shipping certain cellular products including proteins.
-
Microtubules: These hollow rods function primarily to help support and shape the cell. They are important for chromosome movement in mitosis and meiosis, as well as cytosol movement within a cell.
-
Mitochondria: Mitochondria generate energy for the cell by converting glucose (produced by photosynthesis) and oxygen to ATP. This process is known as respiration.
-
Nucleus: The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information (DNA).
-
Nucleolus: This structure within the nucleus helps in the synthesis of ribosomes.
-
Nucleopore: These tiny holes within the nuclear membrane allow nucleic acids and proteins to move into and out of the nucleus.
-
-
Peroxisomes: Peroxisomes are tiny, single membrane bound structures that contain enzymes which produce hydrogen peroxide as a by-product. These structures are involved in plant processes such as photorespiration.
-
Plasmodesmata: These pores or channels are found between plant cell walls and allow molecules and communication signals to pass between individual plant cells.
-
Ribosomes: Consisting of RNA and proteins, ribosomes are responsible for protein assembly. They can be found either attached to the rough ER or free in the cytoplasm.
-
Vacuole: This plant cell organelle provides support for and participates in a variety of cellular functions including storage, detoxification, protection, and growth. When a plant cell matures, it typically contains one large liquid-filled vacuole.
Bailey, Regina. “Learn About Plant Cell Types and How They're Like Animal Cells.” ThoughtCo, www.thoughtco.com/what-is-a-plant-cell-373384.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to create foods from carbon dioxide and water. Photosynthesis in plants generally involves the green pigment chlorophyll and generates oxygen as a byproduct.
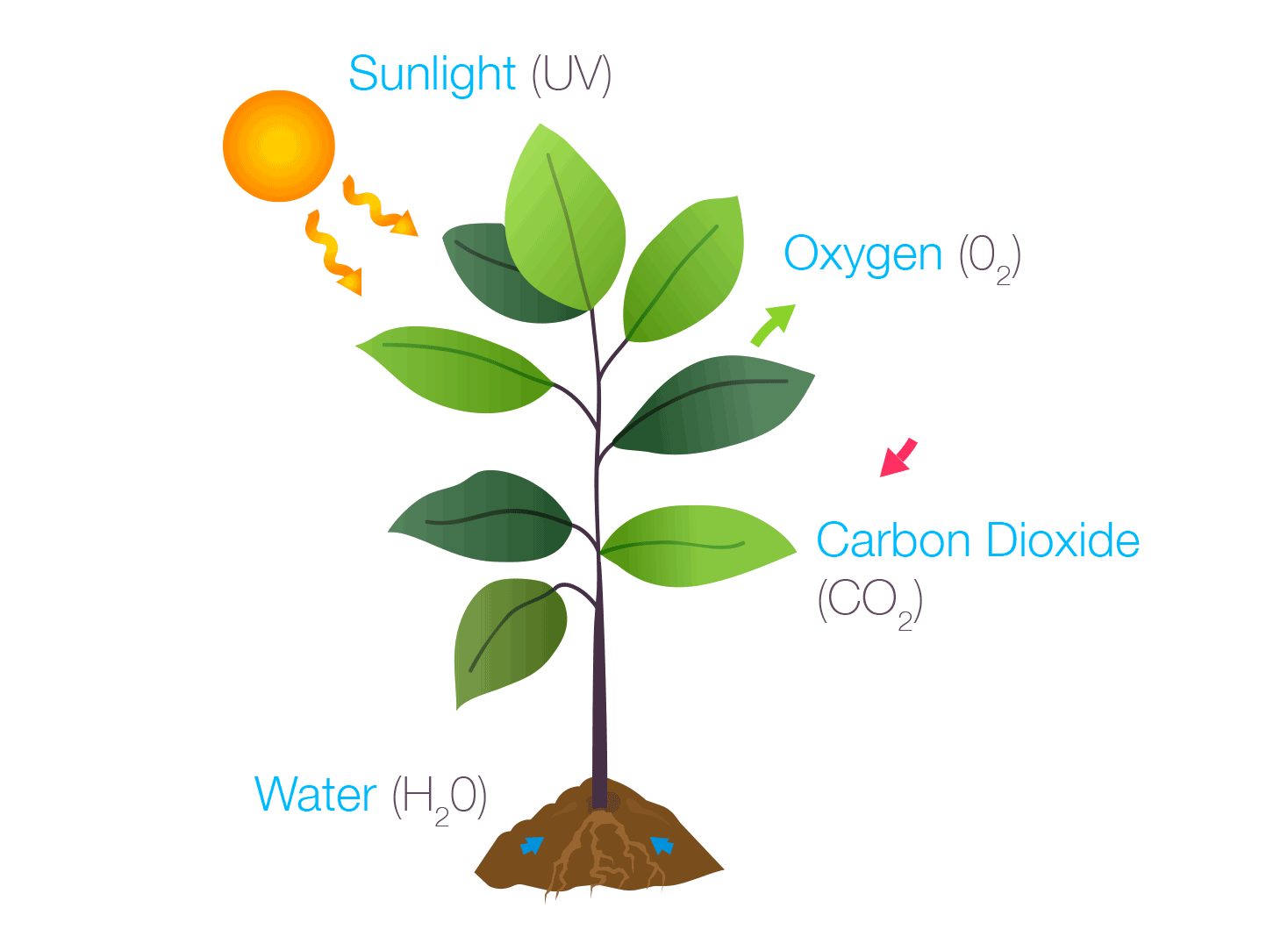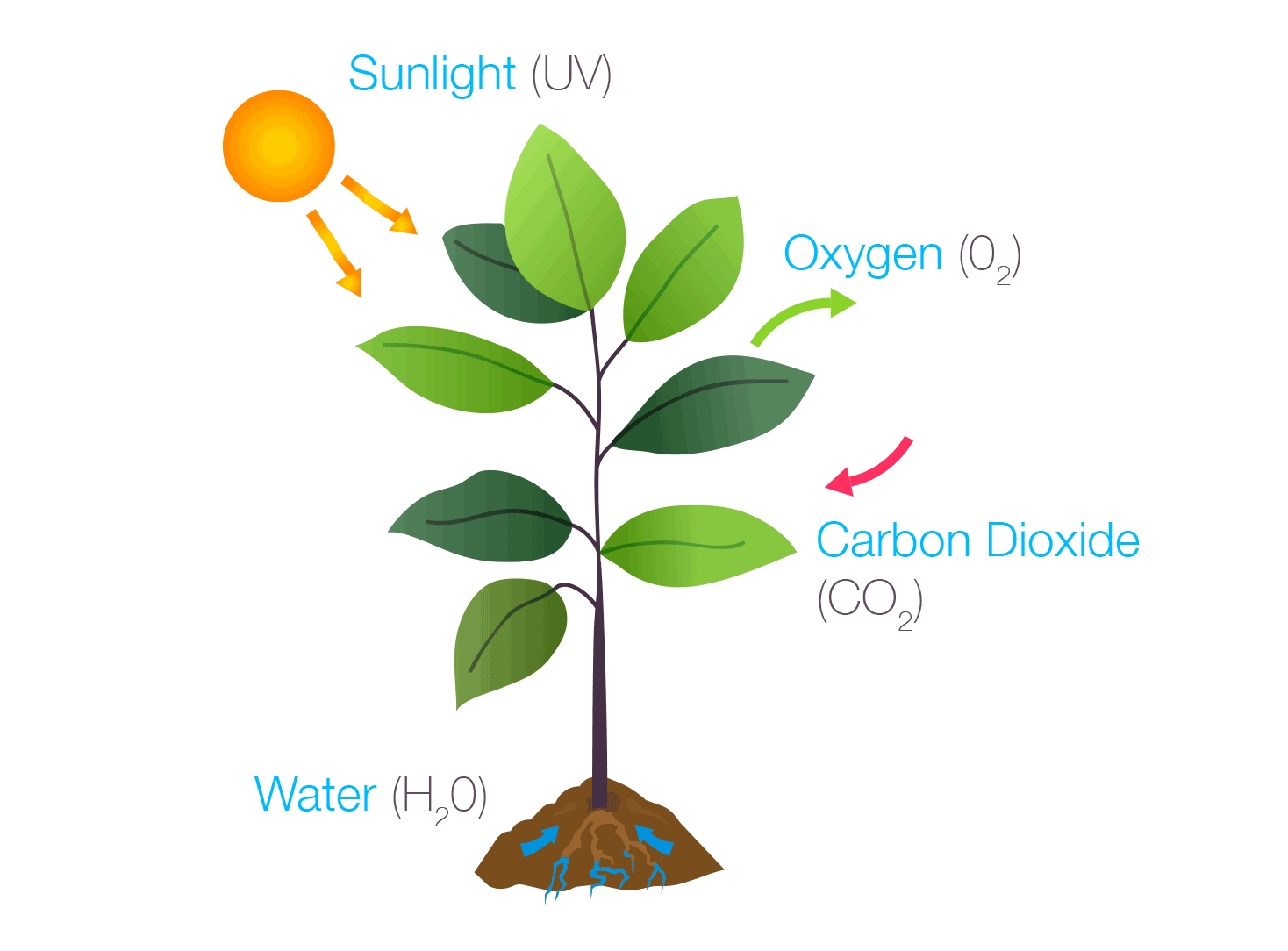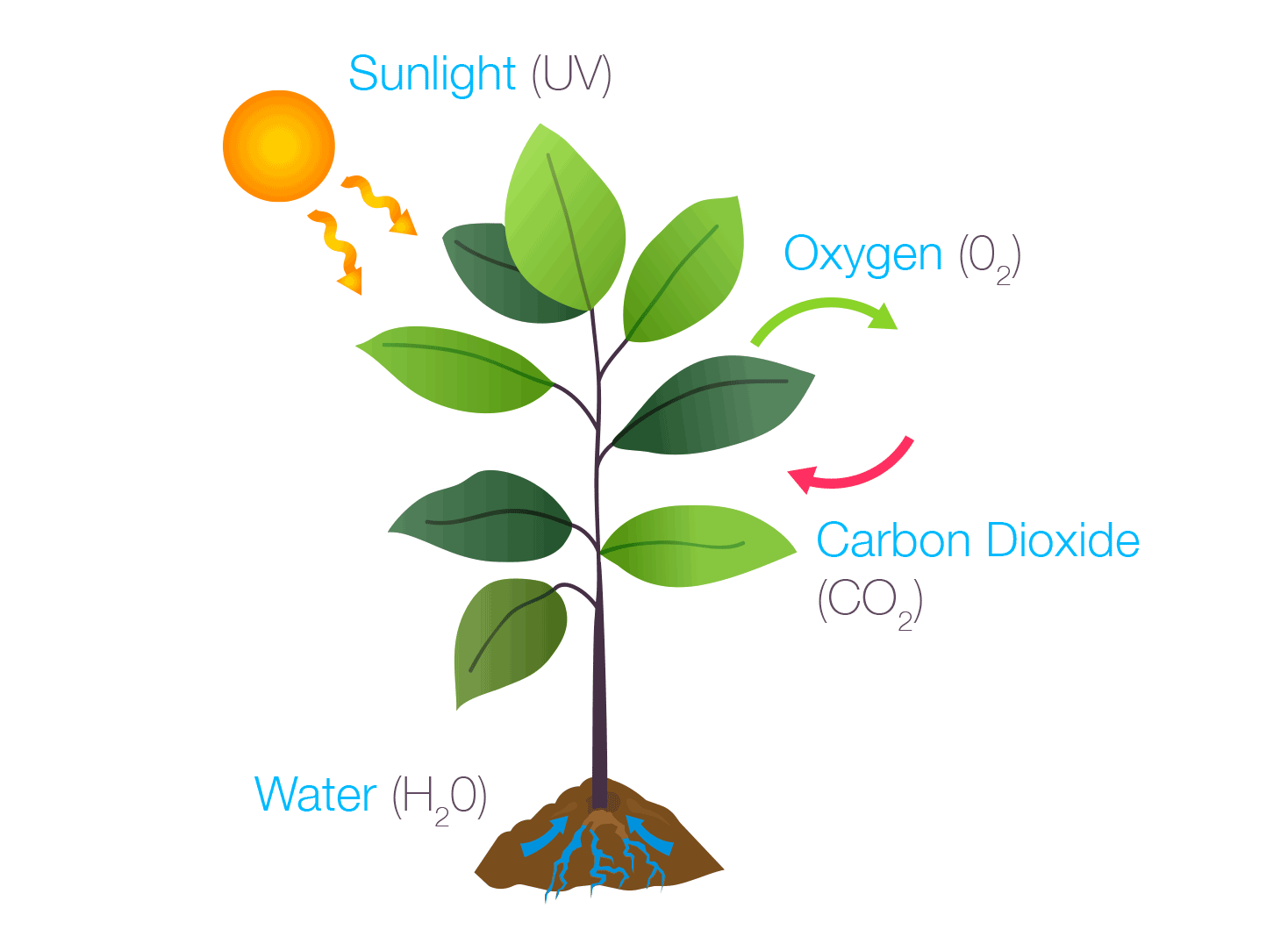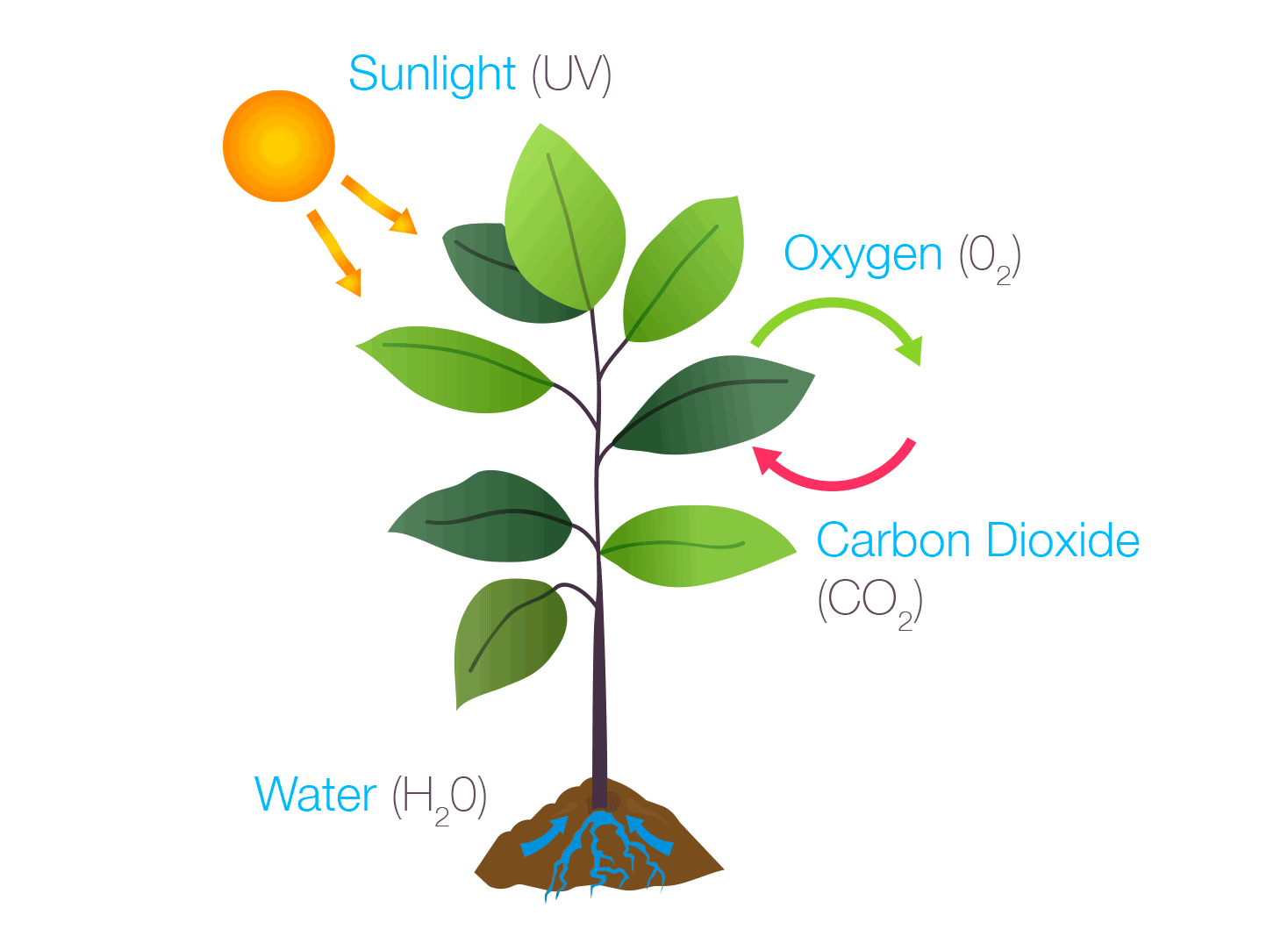
US, Bayer. “Homework Helper: Photosynthesis – The Beaker Life.” The Beaker Life, The Beaker Life, 31 Jan. 2018, thebeakerlife.com/homework-helper-photosynthesis-840ace9e0e3f.

Image Credit: tuksaporn rattanamuk / Shutterstock